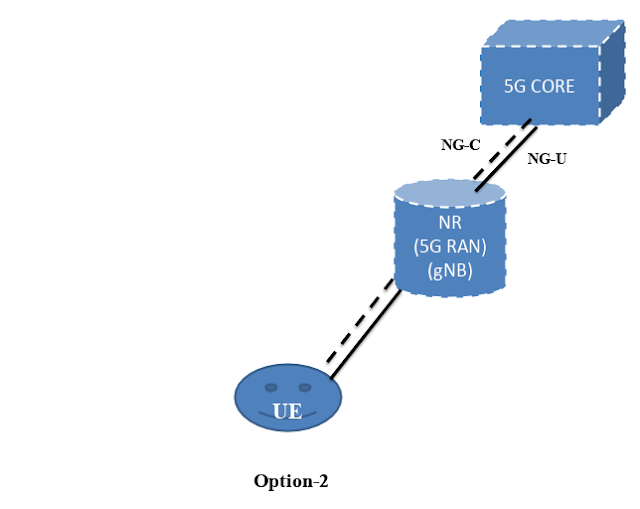
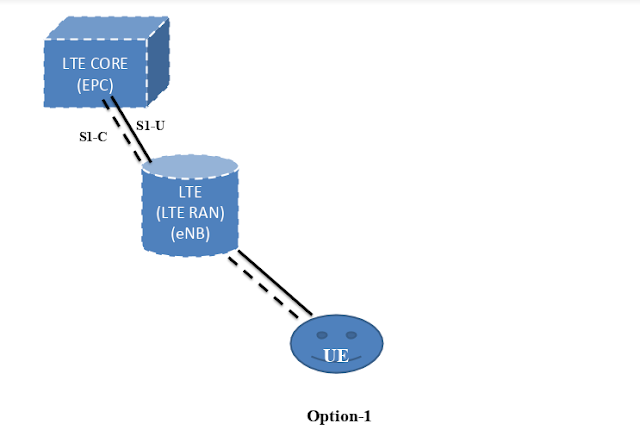
5G Deployment Option-4/4a

Hi Guys today we are learning about 5G deployment options, if you want to know more about other 5G deployment option please click here Option 4: NR-EUTRA Dual Connectivity(NE-DC) Option 4 represents a network using the Next Generation Core (NGC). Control signaling will be routed through the NR RAN. The only difference between Options 4 and 4a is based on whether the user plane data is sent to LTE directly or via the NR RAN. (Difference is UP path Non Standalone (Dual Connectivity 4G/5G)). The pre-requisite conditions for Options 4/4A are eLTE(Release 15) upgrade at the start and a robust 5G coverage. In Option 4/4a, there can be a Dual Connectivity between the gNB (similar role as MeNB in TS 36.300) and the NGC with Non-standalone E-UTRA (similar role as SeNB in TS 36.300). The E-UTRA user plane connection to the NGC can go either via the gNB i.e. Option 4 or directly i.e. Option 4a. The procedures and protocols for the Xn interface b...