Handover Decision
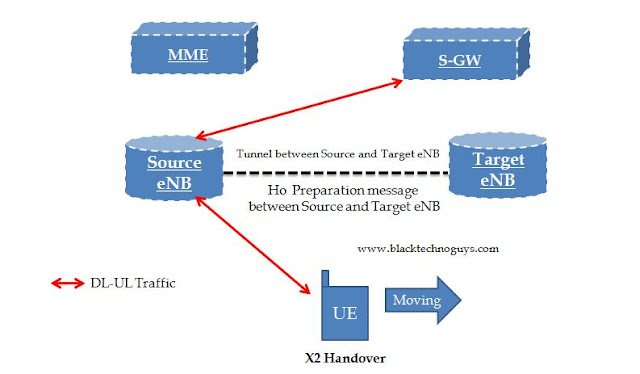
Home LTE NB-IoT 5G(NR-NSA) Handover Decision: As soon as the event A3(for instance) is reported the eNB decides what kind of handover to perform to which target cell and then initiates a handover procedure. Handovers can be classified in many ways one of the classification is as below – (1) Depending on weather EPC Entities that UE is connected to are changed after a handover or not a handover can be categorized as one of the following kinds: (Interview Question: What are the types Handover?) Intra LTE handover – Intra MME/SGW handover – Neither UE’s serving MME nor SGW is changed after handover. Inter LTE handover - UE’s serving MME and/or SGW is changed after handover Inter MME HO: UE’s serving MME is changed, SGW remains unchanged after handover. Inter SGW handover: UE’s ...