Carrier Aggregation Part-2
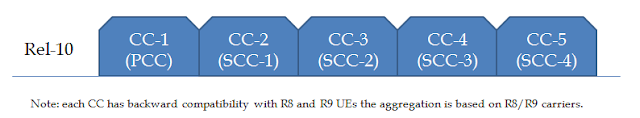
Home LTE NB-IoT 5G(NR-NSA) What is LTE aggregated carriers? The LTE aggregated carriers indicates a combination of maximum PRB and maximum number of CCs ( component carrier) . In R10 and R11 three classes are defined: Class A: PRB ≤ 100, maximum number of CC = 1 Class B: PRB ≤ 100, maximum number of CC = 2 Class C: 100< Nrb ≤ 200, maximum number of CC = 2 Class D: 200< Nrb ≤ 300, maximum number of CC = 3 How many CC support in Bandwidth Class A? one CC How many CC support in Bandwidth Class B? 2 CC How many CC support in Bandwidth Class C? 2 CC What is CA configuration ? The CA configuration indicates a combination of EUTRA operating bands and CA bandwidth class. Let's take some example: For instance the configu...